Call or Text us at
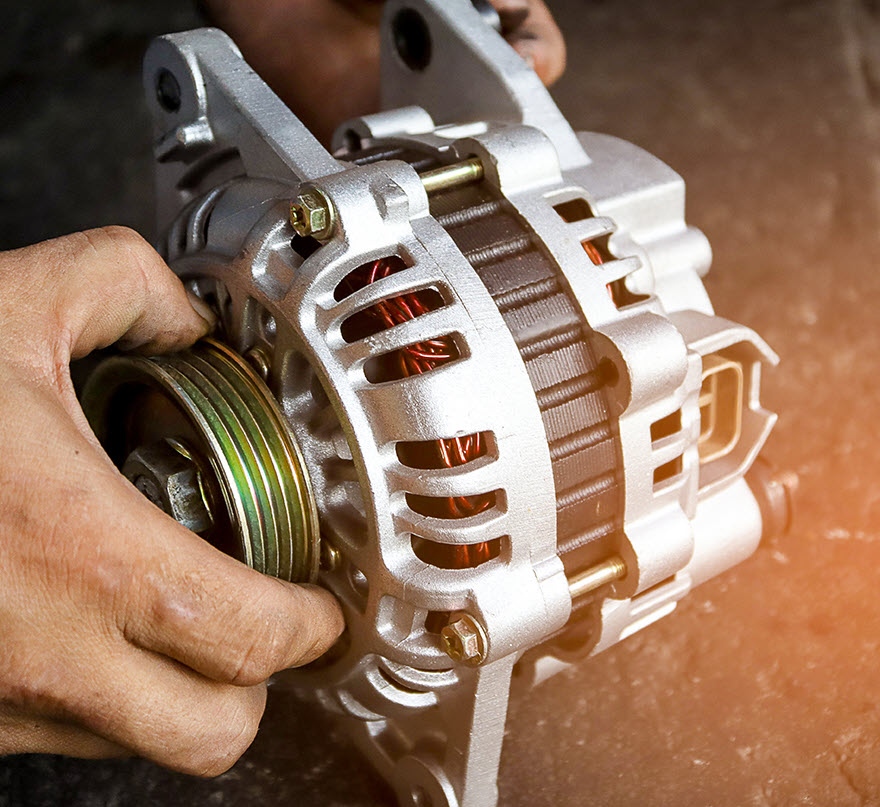


At Beach Auto Repair, our skilled technicians specialize in handling issues
concerning car alternators. Whether it's dimming headlights, electrical failures, or
a worn-out alternator belt, our team swiftly diagnoses the problem and proceeds with
the necessary repairs.
Dimming headlights and electrical malfunctions in your vehicle can be attributed to
a faulty alternator or a worn-out alternator belt. Our experts are skilled at
efficiently and effectively resolving these problems, ensuring optimal charging
system performance and reliable power supply to your vehicle. Feel free to contact
us for top-quality car alternator services that ensure a smooth and uninterrupted
driving experience.
Call or Text us at
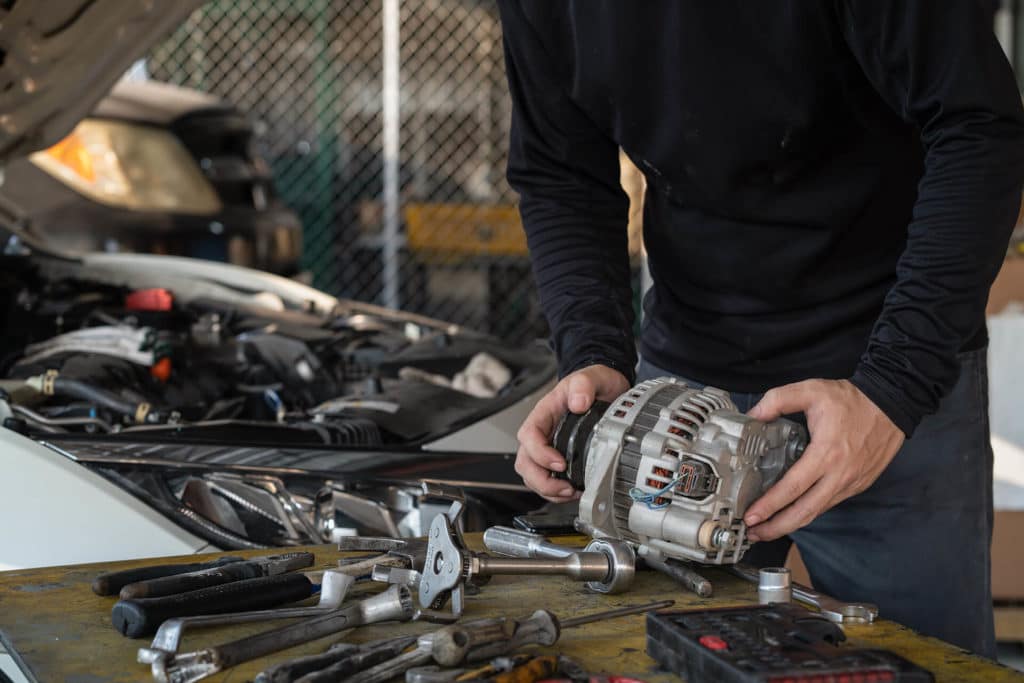
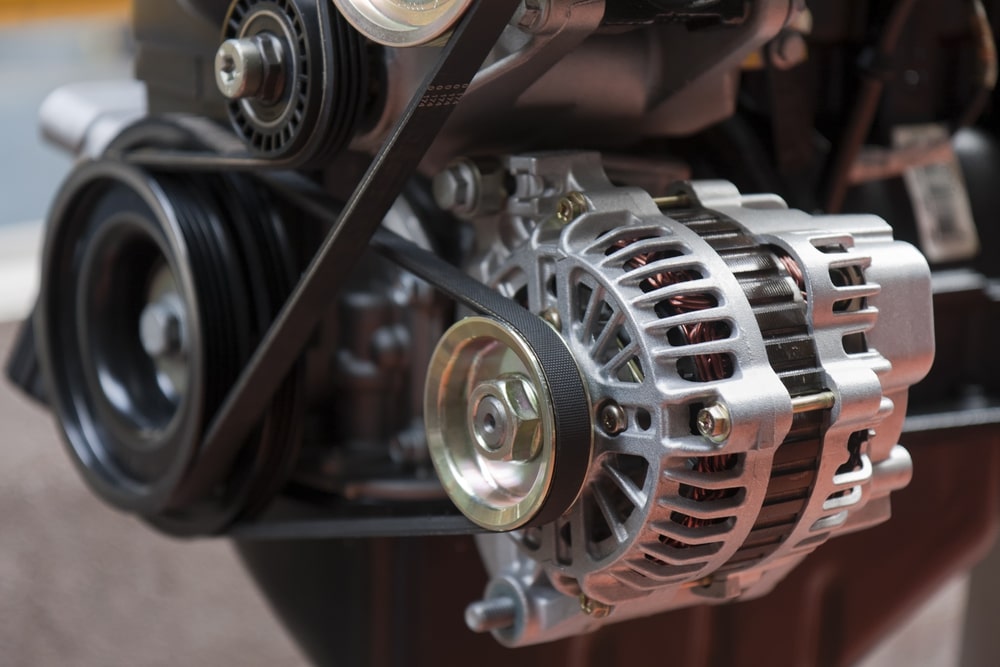


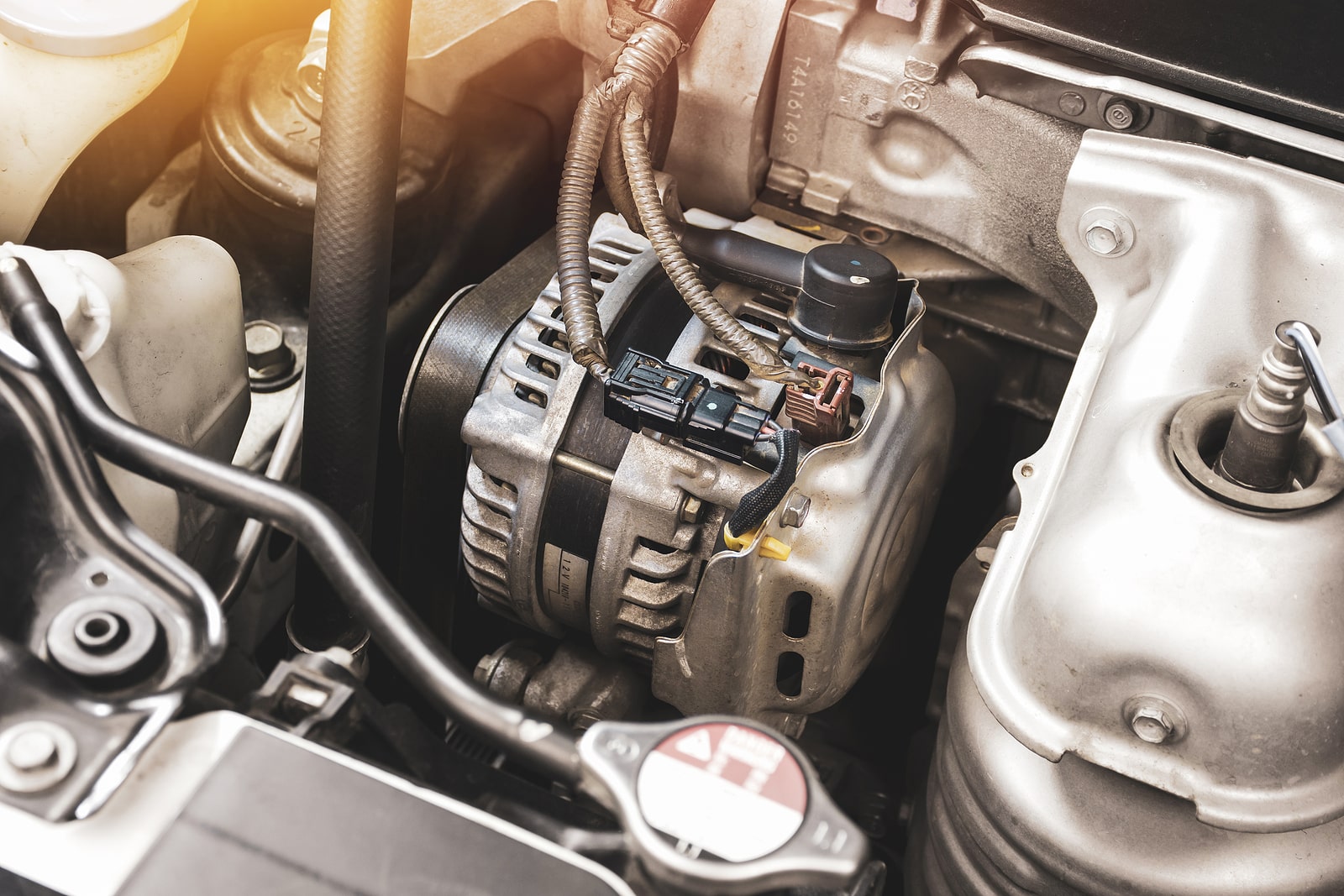
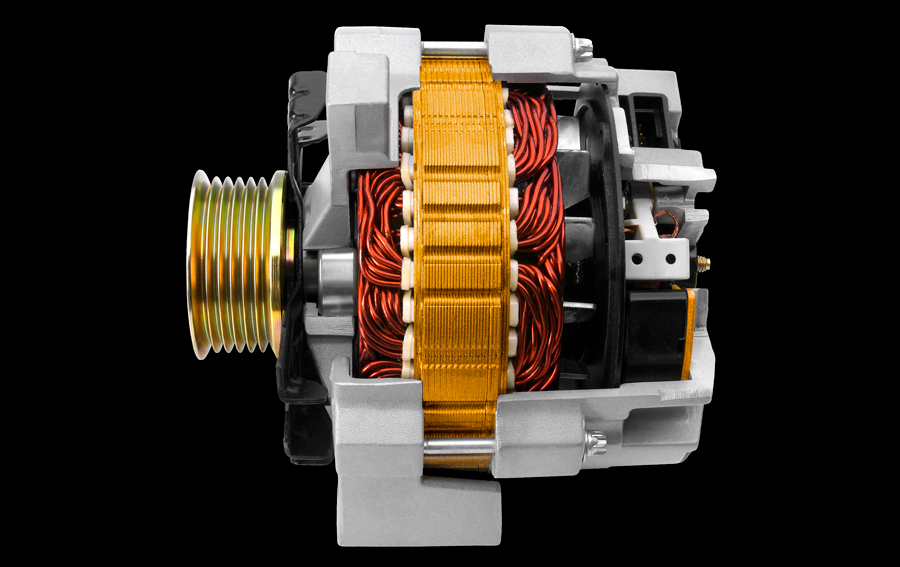
Understanding the purpose of a vehicle's alternator is crucial for grasping its role in generating electrical power. Here are some key points to consider:
1. Electrical Generation: The primary purpose of a vehicle's alternator is to generate electrical power. It converts mechanical energy from the engine's rotation into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is then converted to direct current (DC) to power various electrical systems and charge the battery.
2. Charging the Battery: One of the essential functions of the alternator is to charge the vehicle's battery. As you drive, the alternator ensures that the battery maintains an appropriate charge level, replenishing the energy used to start the engine and power electrical components.
3. Powering Electrical Systems: The alternator provides power to all electrical systems when the engine is running. This includes lights, entertainment systems, power windows, air conditioning, and more. It ensures a continuous supply of electricity for these systems, preventing drain on the battery.
4. Voltage Regulation: The alternator plays a critical role in maintaining a stable voltage level within the vehicle's electrical system. It adjusts its output voltage according to the electrical load and prevents overcharging or undercharging of the battery.
5. Supporting Ignition System: The alternator powers the ignition system, providing the necessary electricity to create sparks in the spark plugs. This ignition process is essential for the combustion of fuel in the engine.
6. Electronic Control Units (ECUs): Modern vehicles rely heavily on electronic control units (ECUs) to manage various functions. The alternator supplies consistent power to these ECUs, ensuring accurate control of engine performance, emissions, and other systems.
7. Accessory Drive System: The alternator is driven by a belt connected to the engine's crankshaft. This accessory drive system converts rotational energy from the engine into electrical energy for powering the vehicle's electrical components.
8. Storing Excess Energy: In some cases, when the electrical load is low and the battery is fully charged, the alternator can produce excess energy. This excess energy is often dissipated as heat, but some vehicles have systems that can use it to improve fuel efficiency, such as regenerative braking in hybrid vehicles.
9. Maintaining Battery Health: The alternator helps keep the battery at an optimal charge level. A properly functioning alternator prevents the battery from becoming undercharged or overcharged, which can extend the battery's lifespan.
10. Emergency Backup: In case of a failing battery, a functioning alternator can provide temporary power to essential systems, allowing you to continue driving for a short period or reach a safe location.
11. Powering Start-Stop Systems: Powering Start-Stop Systems: In vehicles with start-stop technology, the alternator works closely with the system to ensure that the engine restarts quickly and efficiently whenever needed.
12. Hybrid and Electric Vehicles: Hybrid and Electric Vehicles: In hybrid and electric vehicles, the alternator's role might be replaced by a generator or other systems that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy for propulsion or charging the battery.
By understanding the diverse purpose of a vehicle's alternator, you gain insight into its significance in maintaining proper vehicle operation, supporting various electrical systems, and ensuring a reliable driving experience.
Understanding common failures of automotive alternators is vital for maintaining your vehicle's electrical system. Here are some important points to consider:
1. Voltage Regulator Failure: The voltage regulator controls the alternator's output voltage. A failed regulator can result in overcharging or undercharging the battery, leading to electrical system malfunctions and potential damage.
2. Bearing Wear: Alternators contain bearings that allow the rotor to spin. Over time, these bearings can wear out, causing grinding or whining noises. Bearing failure can lead to inefficient alternator operation and potential damage.
3. Faulty Diodes: Alternators use diodes to convert AC current to DC. If diodes fail, they can cause electrical "ripple" that leads to battery drain and irregular voltage output.
4. Worn Brushes: Alternators use brushes to maintain contact with the rotor's slip rings. Worn brushes can lead to intermittent electrical connection, resulting in fluctuating voltage output and potential system failures.
5. Stator or Rotor Failure: The stator and rotor are integral components of the alternator. If either fails due to winding damage, short circuits, or physical issues, the alternator's ability to generate electricity is compromised.
6. Broken or Slipping Belt: A worn or broken belt can prevent the alternator from being driven by the engine's crankshaft. This leads to insufficient charging and can cause the battery to drain.
7. Corroded Terminals: Corrosion on the alternator's electrical terminals can disrupt the flow of electricity between the alternator and the battery, leading to reduced charging efficiency.
8. Insufficient Ventilation: Overheating can occur if the alternator's ventilation system is clogged or damaged. Excessive heat can damage internal components and decrease alternator performance.
9. High Electrical Load: Continuous high demand on the electrical system, such as using multiple high-power accessories simultaneously, can overload the alternator, leading to overheating and potential failure.
10. Age and Wear: Like any mechanical component, alternators have a limited lifespan. Over time, internal components can degrade, leading to reduced performance and eventual failure.
11. Aftermarket Part Quality: Using low-quality or improper aftermarket alternators can lead to early failures. Stick to reputable brands and ensure compatibility with your vehicle's specifications.
12. Poor Battery Health: A weak or failing battery can place additional strain on the alternator, potentially causing it to work harder and wear out faster.
13. Accessory Drive System Issues: If the accessory drive system isn't functioning correctly, it can affect the alternator's performance. A damaged or misaligned belt can lead to reduced charging capability.
14. Improper Repairs: Attempting DIY repairs without proper knowledge can exacerbate issues or introduce new problems. It's advisable to seek professional assistance for complex alternator problems.
By understanding these common alternator failure points, you can take preventive measures to ensure a reliable electrical system, identify issues early, and address them to prevent further damage.
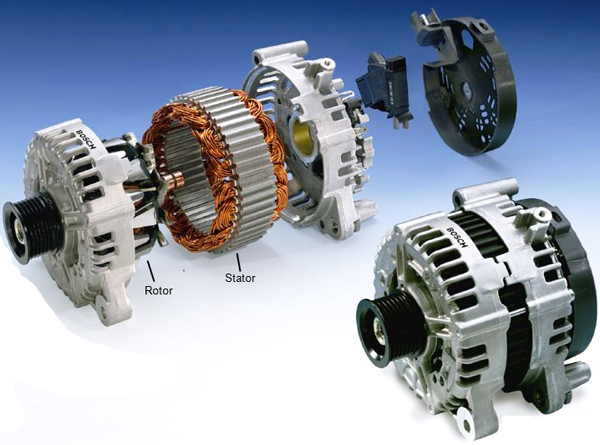
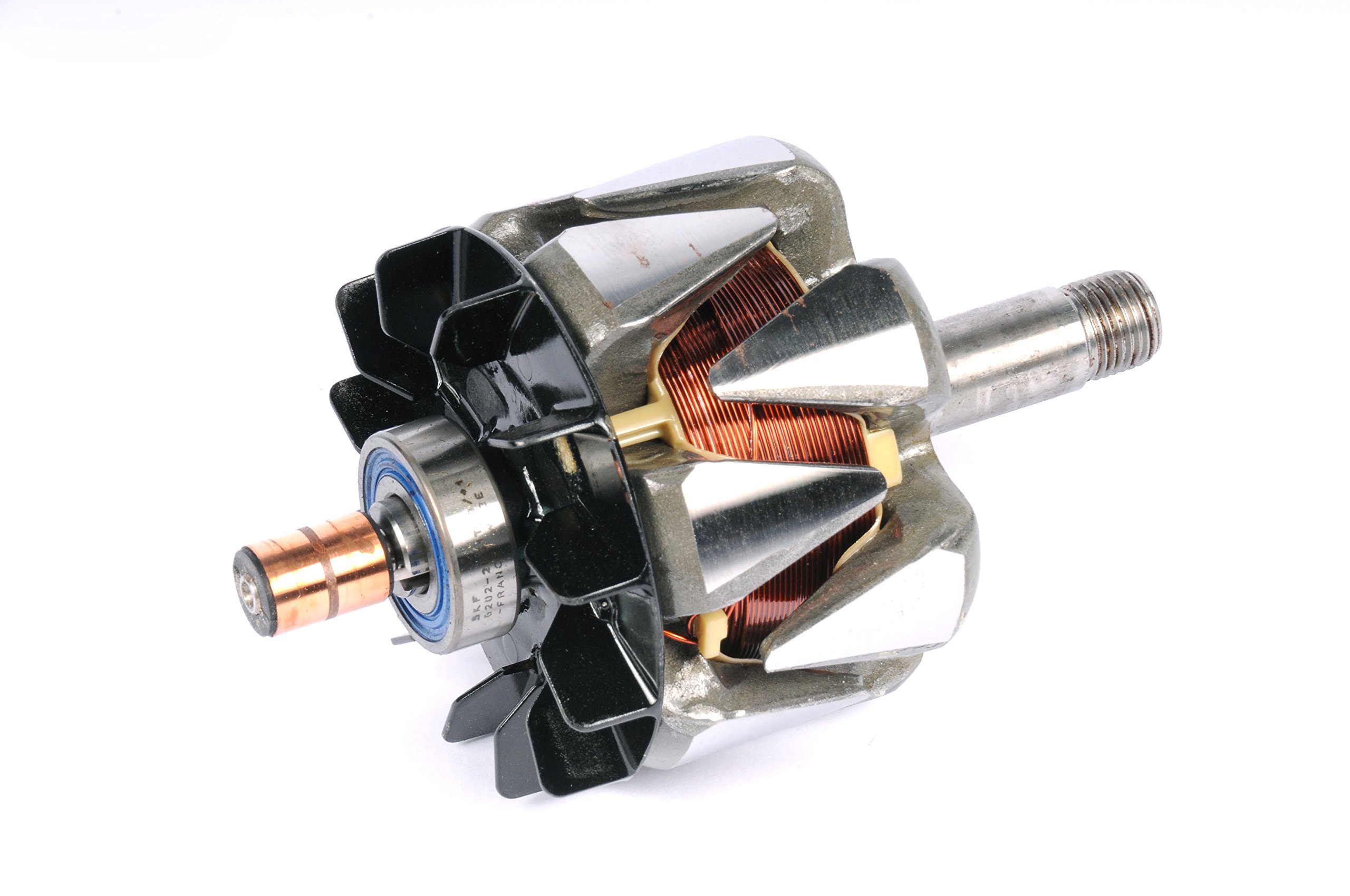
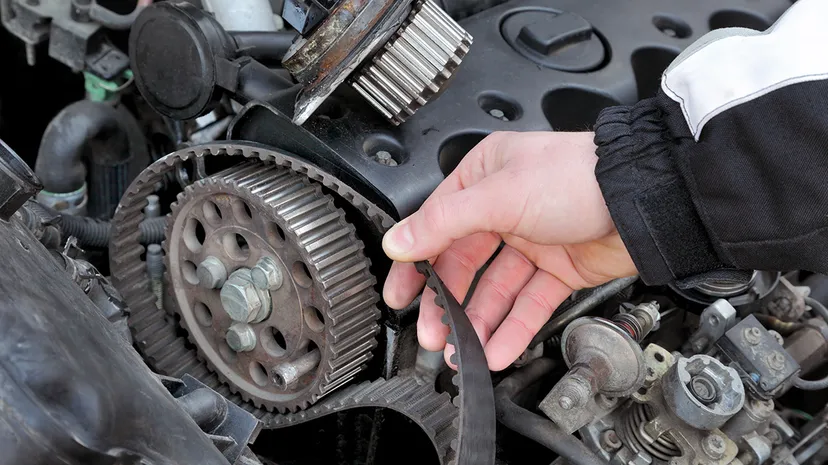



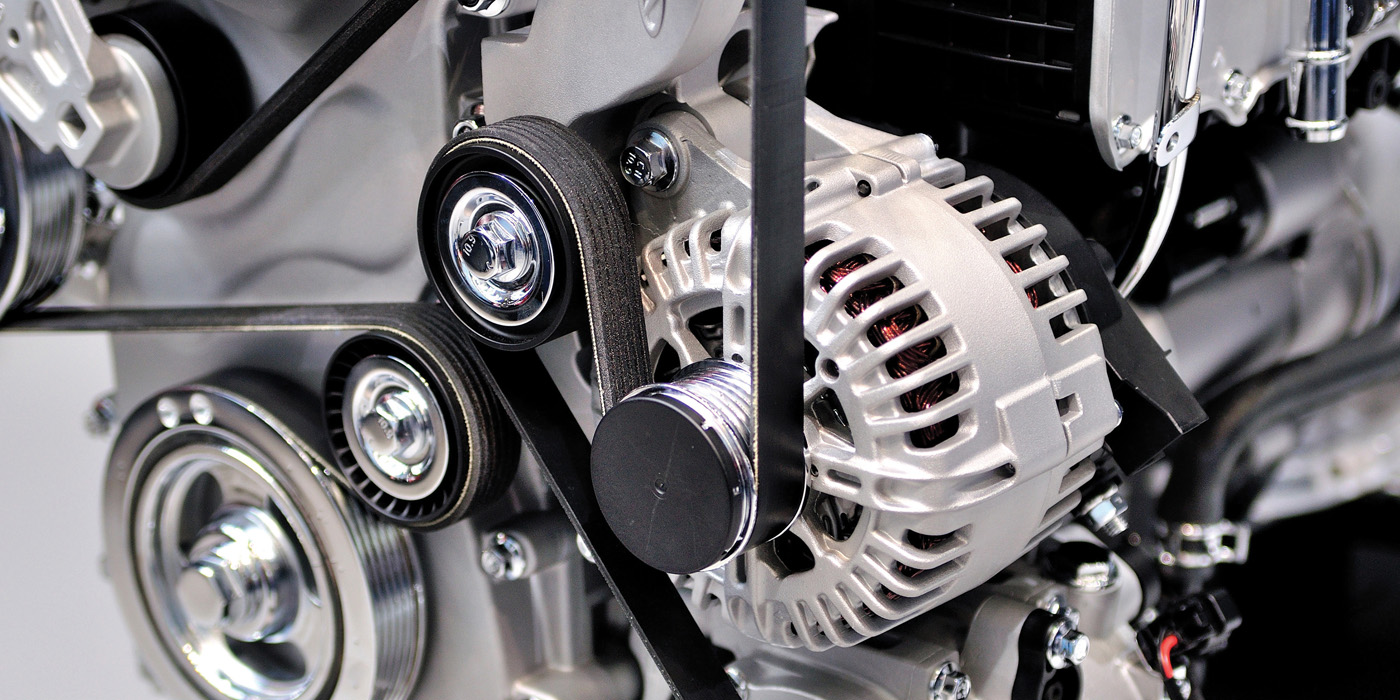


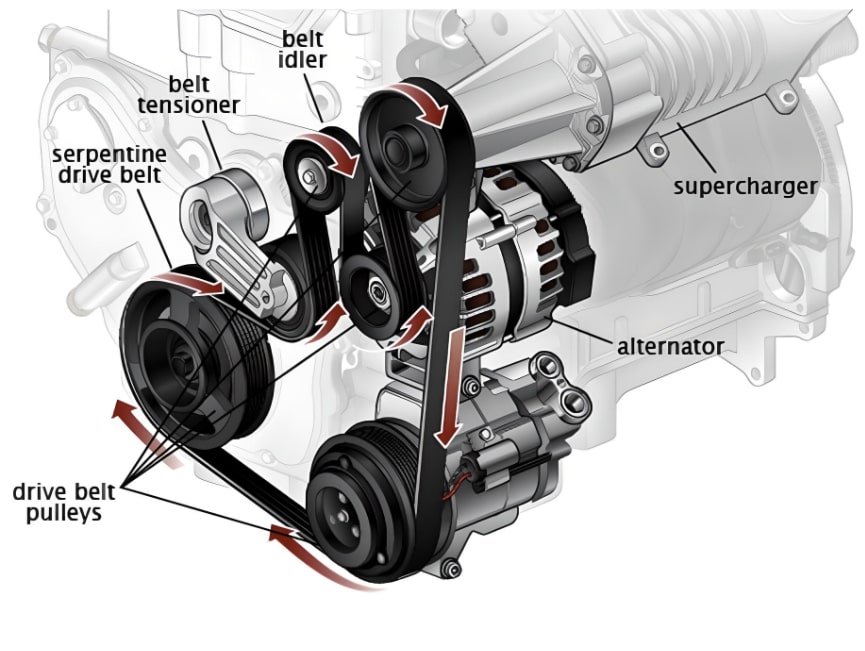



Properly servicing an automotive alternator is essential for maintaining the vehicle's electrical system and overall functionality. Here are some key points to consider:
1. Regular Inspection: Include the alternator in your regular vehicle maintenance routine. Inspect the alternator and its components for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. A visual inspection can often identify potential issues early.
2. Checking Belt Tension: The alternator is driven by a belt connected to the engine's crankshaft. Ensure that the belt is properly tensioned and free from cracks or damage. A loose or worn belt can lead to reduced alternator performance.
3. Testing Output Voltage: Use a multimeter to measure the alternator's output voltage. When the engine is running, the alternator should produce a voltage between 13.5 to 14.5 volts. Significant deviations from this range may indicate a problem.
4. Testing Amperage Output: Test the alternator's amperage output using a clamp meter. The alternator should provide a sufficient amount of current to power the vehicle's electrical systems and charge the battery. Low amperage output could signify a failing alternator.
5. Checking Connections: Inspect the alternator's electrical connections and wiring for tightness and signs of corrosion. Corroded connections can lead to poor electrical contact and reduced charging efficiency.
6. Cleaning Ventilation: Some alternators have ventilation ports or fins to dissipate heat. Ensure these are clean and free from debris, as proper ventilation helps maintain optimal alternator performance.
7. Replacing Faulty Voltage Regulator: The voltage regulator regulates the alternator's output voltage. If you notice voltage fluctuations or abnormal electrical behavior, the voltage regulator might be faulty and need replacement.
8. Addressing Unusual Noises: Unusual noises, such as grinding or whining sounds, could indicate worn bearings inside the alternator. Promptly address such noises to prevent further damage.
9. Professional Inspection: If you suspect alternator issues but aren't experienced in automotive electrical systems, consult a professional mechanic. They can perform in-depth tests and diagnostics to identify specific problems.
10. Bearing Replacement: If you're skilled in automotive repair, you might consider replacing worn alternator bearings. However, this can be a complex task, and if not done correctly, it can lead to further damage.
11. Balancing Electrical Load: Excessive electrical load can strain the alternator. Avoid running high-demand electrical components simultaneously, as this could lead to overheating and reduced alternator lifespan.
12. Preventive Maintenance: In regions with extreme temperatures or demanding conditions, consider preventive alternator maintenance, such as replacing brushes and cleaning components.
13. Replacement: If the alternator is severely damaged or no longer functioning within specifications, replacement might be the best option. Consult your vehicle's manual or a professional mechanic for suitable replacement options.
14. Battery Health: An alternator's performance can be affected by the condition of the battery. Ensure your vehicle's battery is in good health to prevent unnecessary strain on the alternator.
By understanding these key points and staying proactive in servicing your automotive alternator, you can maintain a reliable electrical system, prevent unexpected breakdowns, and ensure your vehicle operates smoothly.
Let us know how we can help.